After Tax Real Rate Of Return Definition And How To Calculate It
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 9 min read
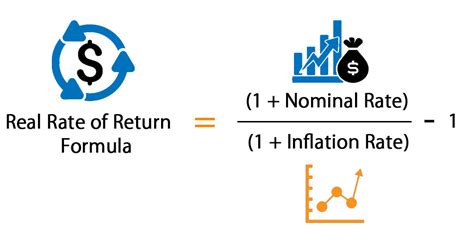
Table of Contents
Unveiling the True Power of Your Investments: Understanding and Calculating the After-Tax Real Rate of Return
What truly reflects the growth of your investments, considering both taxes and inflation?
The after-tax real rate of return provides a clear, unvarnished picture of your investment's actual growth, stripping away the illusions of nominal gains.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to the after-tax real rate of return was published today, providing up-to-date insights and calculations for investors of all levels.
Why the After-Tax Real Rate of Return Matters
Many investors focus solely on the nominal rate of return – the percentage increase in the investment's value before accounting for taxes and inflation. However, this figure can be misleading. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, while taxes significantly reduce the actual amount of profit you retain. Ignoring these crucial factors paints an incomplete and potentially inaccurate picture of investment performance. Understanding the after-tax real rate of return is essential for making informed financial decisions, comparing different investment options effectively, and ensuring your investments truly grow your wealth. This metric offers a realistic assessment of your investment's success, allowing for better planning and more accurate projections of future financial security. It's the key to unlocking a true understanding of your investment's power.
Overview of this Article
This article delves into the intricacies of the after-tax real rate of return. We will explore its definition, the step-by-step calculation process, the impact of different tax brackets, and offer practical examples to illustrate its application. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of this critical financial metric and learn how to use it to evaluate their investment strategies effectively. The article also touches on the complexities surrounding capital gains taxes and their influence on the final calculation.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The information presented in this article is based on extensive research, drawing upon established financial principles, tax regulations, and economic theories. Data from reputable sources, including government publications and financial journals, has been utilized to ensure accuracy and clarity.
Key Takeaways
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Nominal Rate of Return | The percentage increase in investment value before considering taxes and inflation. |
| Real Rate of Return | The percentage increase in investment value after adjusting for inflation. |
| After-Tax Real Rate of Return | The percentage increase in investment value after adjusting for both taxes and inflation, representing the true growth of your investment's purchasing power. |
| Tax Bracket | The range of income subject to a specific tax rate. |
| Capital Gains Tax | Tax levied on profits from the sale of assets, such as stocks or bonds. |
| Inflation Rate | The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling. |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Let's now delve into the core components of calculating the after-tax real rate of return, starting with a clear definition and then progressing through the step-by-step calculation process.
Exploring the Key Aspects of After-Tax Real Rate of Return
-
Understanding the Components: The calculation involves three key elements: the nominal rate of return, the tax rate, and the inflation rate. Each plays a critical role in determining the final after-tax real rate of return.
-
The Role of Taxes: Taxes significantly impact the final return. Different asset classes and investment types are subject to various tax rates. Understanding your applicable tax bracket and the specific tax implications of your investments is crucial. For example, capital gains taxes are applied to profits from the sale of assets, and these rates can vary depending on the holding period of the asset.
-
Inflation's Impact: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. A 10% nominal return is less impressive if inflation is also at 5%, as your real gain is only 5%. This is why adjusting for inflation is vital in accurately assessing investment performance.
-
Calculation Methodology: The precise calculation involves a multi-step process, as we will detail below. It requires careful attention to detail and accurate data to arrive at a reliable result.
-
Interpreting the Results: Once calculated, the after-tax real rate of return provides a clear picture of the actual growth of your investment, adjusted for both taxes and the effects of inflation. This figure allows for meaningful comparisons between different investments and helps you make informed decisions about your investment strategy.
Calculating the After-Tax Real Rate of Return: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Determine the Nominal Rate of Return: Calculate the percentage increase in your investment's value over a specific period. This is a simple calculation: [(Ending Value - Beginning Value) / Beginning Value] x 100.
-
Calculate the After-Tax Nominal Rate of Return: Subtract your applicable tax rate from your nominal rate of return. For example, if your nominal return is 10% and your tax rate is 20%, your after-tax nominal return is 8% (10% x (1 - 0.20)). Remember to account for the specific tax implications relevant to your investment type (e.g., capital gains taxes, dividend taxes).
-
Determine the Inflation Rate: Find the inflation rate for the same period as your investment. This data is readily available from government sources like the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) in the United States or equivalent agencies in other countries.
-
Calculate the After-Tax Real Rate of Return: This step utilizes the following formula:
After-Tax Real Rate of Return = [(1 + After-Tax Nominal Rate of Return) / (1 + Inflation Rate)] - 1
This formula accounts for the compounding effect of both inflation and the after-tax nominal return.
-
Express the Result as a Percentage: Multiply the result by 100 to express the after-tax real rate of return as a percentage.
Example Calculation
Let's assume an investment had a nominal rate of return of 12% over one year. The investor's tax rate is 25%, and the inflation rate for that year was 3%.
-
Nominal Rate of Return: 12%
-
After-Tax Nominal Rate of Return: 12% x (1 - 0.25) = 9%
-
Inflation Rate: 3%
-
After-Tax Real Rate of Return: [(1 + 0.09) / (1 + 0.03)] - 1 = 0.0583 or 5.83%
Therefore, the after-tax real rate of return for this investment is 5.83%. This means the investment truly grew by 5.83% in terms of purchasing power, after accounting for both taxes and inflation.
Exploring the Connection Between Capital Gains Taxes and After-Tax Real Rate of Return
Capital gains taxes significantly affect the after-tax real rate of return, especially for investments held for shorter periods. The tax rate applied to capital gains varies depending on the holding period of the asset (short-term vs. long-term) and the investor's income bracket. It's crucial to account for these specific tax implications during the calculation process to obtain an accurate reflection of the investment's true return. For instance, short-term capital gains are often taxed at a higher rate than long-term capital gains.
Further Analysis of Inflation's Impact
Inflation's impact on investment returns cannot be overstated. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of your returns, making it crucial to adjust for this factor when evaluating investment performance. Understanding the historical inflation rates and projecting future inflation expectations is essential for effective financial planning and investment decision-making. Unexpectedly high inflation can significantly reduce the real return of an investment, highlighting the importance of accurately forecasting this critical economic indicator.
FAQ Section
-
Q: Why is the after-tax real rate of return more important than the nominal rate of return?
A: The nominal rate doesn't account for taxes and inflation, which significantly impact your actual gains. The after-tax real rate offers a more accurate picture of your investment's true growth.
-
Q: How do I find the inflation rate for a specific period?
A: Check the website of your country's central bank or statistical agency (e.g., BLS in the US).
-
Q: What happens if the inflation rate is higher than the nominal rate of return?
A: Your after-tax real rate of return will be negative, meaning your investment lost purchasing power.
-
Q: Does the after-tax real rate of return apply to all investment types?
A: Yes, though the specific tax implications will vary based on the investment type (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.).
-
Q: How frequently should I calculate my after-tax real rate of return?
A: Annually is a good practice, especially for long-term investments.
-
Q: Can I use online calculators to compute the after-tax real rate of return?
A: Yes, many financial websites offer calculators to simplify the process. However, always double-check the input data and understand the underlying formulas.
Practical Tips
-
Track your investments: Keep meticulous records of your investments’ purchase price, sale price, and all associated fees.
-
Understand your tax obligations: Consult a tax professional to understand the tax implications of your investments.
-
Monitor inflation rates: Stay informed about current and projected inflation rates.
-
Diversify your portfolio: Diversification can help mitigate the risk of inflation eroding your returns.
-
Consider inflation-protected securities: Explore investments designed to protect against inflation, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS).
-
Regularly review your investment strategy: Based on your after-tax real rate of return, adjust your strategy as needed.
-
Use financial planning tools: Leverage software or online calculators to streamline the calculation process.
-
Seek professional advice: Consult a financial advisor for personalized guidance.
Final Conclusion
The after-tax real rate of return is not merely a financial metric; it's a vital tool for assessing the true success of your investments. By understanding its calculation and incorporating it into your investment planning, you gain a clearer picture of your financial progress, paving the way for more informed decisions and a more secure financial future. Don't let inflation and taxes obscure the true growth of your wealth; use the after-tax real rate of return to unlock the true power of your investments. The insights gleaned from this comprehensive analysis empower you to navigate the complexities of the financial world with greater confidence and achieve your long-term financial objectives.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about After Tax Real Rate Of Return Definition And How To Calculate It . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.