How Does Currency Hedging Work
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
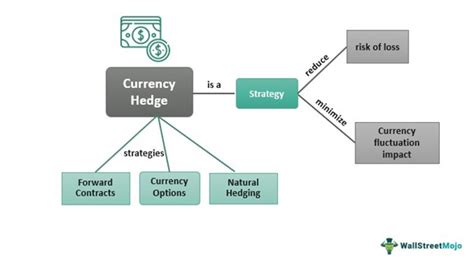
Table of Contents
De-Risking Your Global Investments: How Currency Hedging Works
What makes currency hedging a crucial strategy for international investors?
Currency hedging is not just a sophisticated financial tool; it's a vital risk management technique that can significantly impact the profitability and stability of global investment portfolios.
Editor’s Note: This article on currency hedging was published today, providing up-to-date insights into this critical financial strategy.
Why Currency Hedging Matters
In today's interconnected global economy, businesses and investors frequently engage in cross-border transactions. This involves converting currencies, exposing them to fluctuations in exchange rates. These fluctuations, even seemingly minor ones, can significantly impact the profitability of international investments and trade. Currency hedging aims to mitigate this risk, ensuring that the returns from foreign investments are not eroded by adverse movements in exchange rates. It's not about speculating on currency movements; it's about protecting existing gains and minimizing potential losses. The importance of currency hedging extends across various sectors, from multinational corporations managing global supply chains to individual investors holding international stocks or bonds. For example, an American company exporting goods to Europe faces exchange rate risk: if the Euro weakens against the dollar, their profits in dollars will be lower than anticipated. Hedging helps them lock in a favorable exchange rate, protecting their revenue stream.
Overview of the Article
This article provides a comprehensive overview of currency hedging, exploring its underlying principles, various techniques, and practical applications. Readers will gain an understanding of different hedging instruments, the factors influencing hedging decisions, and the potential benefits and limitations of this strategy. We will also delve into the relationship between currency hedging and other risk management tools and address frequently asked questions regarding its implementation.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, including analysis of market data, academic literature on financial risk management, and insights from industry professionals specializing in foreign exchange (forex) trading and risk mitigation. The information presented is designed to be both informative and practically relevant to a broad audience, regardless of their prior knowledge of financial markets.
Key Takeaways
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Exchange Rate Risk (Forex Risk) | The risk that the value of one currency will fluctuate against another, impacting the value of investments. |
| Hedging | Techniques used to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on financial assets or transactions. |
| Forward Contracts | Agreements to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a future date. |
| Futures Contracts | Standardized contracts traded on exchanges, offering flexibility and liquidity for hedging. |
| Options Contracts | Contracts granting the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell currency at a specified rate. |
| Currency Swaps | Agreements to exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies over a specified period. |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Let’s now delve into the core mechanisms of currency hedging, beginning with an explanation of the types of exchange rate risk and the different instruments used to manage them.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Currency Hedging
-
Understanding Exchange Rate Risk: There are two main types of exchange rate risk: transaction risk and translation risk. Transaction risk involves the risk of losses arising from foreign currency transactions, such as importing or exporting goods. Translation risk refers to the risk that the value of a company's foreign subsidiaries' assets and liabilities will change due to exchange rate fluctuations when translated back into the reporting currency.
-
Hedging Instruments: A range of financial instruments can be used for currency hedging, each with its own characteristics and suitability for different situations. These include forward contracts, futures contracts, options contracts, and currency swaps.
-
Forward Contracts: These are private agreements between two parties to exchange currencies at a predetermined exchange rate (the forward rate) on a specific future date. They offer certainty but lack the liquidity of exchange-traded instruments.
-
Futures Contracts: These are standardized contracts traded on exchanges, offering greater liquidity and flexibility than forward contracts. They allow for hedging against exchange rate movements over specific periods. However, they might not perfectly match the specific needs of the hedger.
-
Options Contracts: These give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a currency at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). Options provide flexibility as the hedger can choose whether to exercise the option depending on market conditions.
-
Currency Swaps: These are agreements to exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies over a specified period. They are commonly used by companies with substantial foreign currency debt or assets. They can help reduce the cost of borrowing in foreign currencies.
Closing Insights
Currency hedging is a powerful tool for mitigating the financial risks associated with international transactions and investments. The choice of hedging instrument depends on the specific circumstances, including the size and duration of the exposure, the level of risk tolerance, and market conditions. While hedging reduces risk, it doesn’t eliminate it entirely and may involve costs, such as premiums for options contracts or spreads between spot and forward rates. Effective hedging requires careful consideration of various factors and professional guidance for complex scenarios. Understanding the nuances of different hedging strategies is crucial for successful international business and investment management.
Exploring the Connection Between Diversification and Currency Hedging
Diversification, a core principle of investment management, involves spreading investments across different asset classes and geographies to reduce overall portfolio risk. Currency hedging plays a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of diversification. While diversification reduces risk by spreading exposure across different currencies, hedging further mitigates the risk associated with exchange rate fluctuations. For example, an investor with a diversified portfolio including assets denominated in multiple currencies can use hedging techniques to protect the value of these assets against adverse currency movements, thus optimizing their overall risk-return profile.
Further Analysis of Diversification
Diversification's benefits extend beyond currency risk management. By spreading investments across different assets (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.), industries, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of individual asset underperformance on their overall portfolio. The relationship between diversification and risk is inversely proportional: greater diversification generally leads to lower portfolio risk. However, it’s crucial to note that diversification doesn’t eliminate risk entirely. Market downturns can still impact diversified portfolios, albeit typically to a lesser extent than undiversified portfolios. The effectiveness of diversification also depends on the degree of correlation between assets in the portfolio. Assets with low or negative correlations provide greater diversification benefits.
| Diversification Strategy | Description | Impact on Currency Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Global Equity Diversification | Investing in stocks from multiple countries | Reduced, but not eliminated, by hedging |
| International Bond Diversification | Investing in bonds issued by governments or corporations in different countries | Reduced, but not eliminated, by hedging |
| Currency Diversification | Holding assets and liabilities in different currencies | Potentially reduced, enhanced by hedging |
FAQ Section
Q1: Is currency hedging always necessary?
A1: No, currency hedging is not always necessary. The decision to hedge depends on factors such as risk tolerance, the duration of the foreign currency exposure, and the potential impact of exchange rate fluctuations on profitability.
Q2: What are the costs associated with currency hedging?
A2: Hedging involves costs, such as premiums for options, spreads between spot and forward rates, and transaction fees. These costs must be weighed against the potential benefits of risk reduction.
Q3: How can I choose the right hedging strategy?
A3: The optimal hedging strategy depends on several factors, including your risk profile, the nature and duration of your foreign currency exposure, and market conditions. Consulting a financial advisor experienced in foreign exchange markets is recommended.
Q4: Can hedging eliminate all currency risk?
A4: No, hedging cannot entirely eliminate currency risk, but it significantly reduces it. Unexpected and extreme market events can still impact hedged positions.
Q5: What are the potential downsides of hedging?
A5: While hedging reduces risk, it also limits potential upside. If exchange rates move favorably, the hedged position may not benefit from those gains.
Q6: Are there any circumstances where hedging might be counterproductive?
A6: In certain situations, such as short-term exposures or when forecasting exchange rate movements with high confidence, hedging might be unnecessary or even detrimental due to the associated costs.
Practical Tips
-
Assess your exposure: Identify all your foreign currency transactions and investments to determine your overall exposure to exchange rate risk.
-
Define your risk tolerance: Establish how much risk you are willing to accept, considering your investment goals and overall financial situation.
-
Choose appropriate hedging instruments: Select the hedging instrument that best suits your needs and risk profile, considering factors such as liquidity, cost, and flexibility.
-
Monitor market conditions: Keep abreast of market movements and economic factors that can impact exchange rates. Regularly review your hedging strategy and make adjustments as needed.
-
Diversify your hedging strategies: Don’t rely on a single hedging instrument; use a combination of techniques to spread the risk.
-
Seek professional advice: Consult with a financial advisor or forex specialist to develop a customized hedging strategy tailored to your specific circumstances.
-
Consider using stop-loss orders: To limit potential losses, you can place stop-loss orders to automatically close your hedged positions if exchange rates move against your expectations.
-
Regularly review and adjust your strategy: Market conditions change constantly; it's crucial to regularly review and adjust your hedging strategy to ensure it continues to be effective.
Final Conclusion
Currency hedging is a multifaceted risk management strategy that plays a critical role in protecting international investments and transactions from the volatility of exchange rates. By carefully considering various hedging techniques and aligning them with risk tolerance and investment goals, businesses and individuals can significantly reduce their exposure to currency fluctuations and enhance the overall profitability and stability of their global financial endeavors. While hedging involves costs, the potential benefits in mitigating potentially significant losses often outweigh these costs. A comprehensive understanding of currency hedging principles is crucial for navigating the complexities of the global financial landscape. Further exploration into specific hedging techniques and their applications within different financial contexts can enhance investment decision-making and foster greater financial security in an increasingly interconnected world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does Currency Hedging Work . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.