How To Buy Credit Default Swaps
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
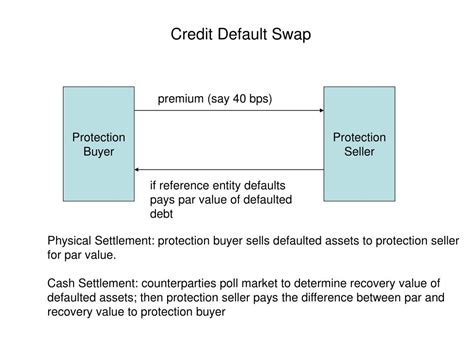
Table of Contents
How to Buy Credit Default Swaps: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating the CDS Market
What makes understanding Credit Default Swaps (CDS) crucial for sophisticated investors?
Credit Default Swaps (CDS) offer a powerful tool for managing credit risk, but navigating this complex market requires careful planning and a deep understanding of its intricacies.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to buying credit default swaps has been published today.
Why Credit Default Swaps Matter
Credit Default Swaps (CDS) are derivative contracts that allow investors to transfer credit risk associated with a specific debt instrument (e.g., a corporate bond or loan) to another party. Their importance stems from their ability to:
- Hedge Credit Risk: Companies and investors can use CDS to protect themselves against potential defaults on bonds or loans they hold. If the underlying debt defaults, the CDS buyer receives a payout, offsetting the loss.
- Speculate on Creditworthiness: While primarily a hedging tool, CDS can also be used for speculative purposes. Investors who believe a company is likely to default can buy a CDS, profiting if their prediction is correct.
- Enhance Portfolio Diversification: CDS contracts can diversify a portfolio, reducing overall credit risk exposure and improving risk-adjusted returns.
- Liquidity Provision: The CDS market offers liquidity, allowing investors to adjust their credit exposure quickly and efficiently. This is particularly important in times of market stress.
- Arbitrage Opportunities: Differences in pricing across CDS contracts on the same underlying debt can create arbitrage opportunities for sophisticated investors.
This article explores the key aspects of buying credit default swaps, including the process, considerations, risks, and regulatory landscape. Readers will gain actionable insights and a deeper understanding of this complex but crucial financial instrument.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is based on extensive research, drawing upon reputable sources such as industry reports from organizations like the International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA), academic publications on credit derivatives, and insights from financial professionals specializing in fixed income and derivatives trading. A structured approach has been employed to present information clearly and accurately.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Insight |
|---|---|
| Understanding CDS Structure | CDS contracts involve a buyer and a seller; the buyer pays premiums, and the seller compensates for defaults. |
| Market Access | Access typically requires sophisticated financial knowledge, substantial capital, and brokerage relationships. |
| Risk Management | CDS trading involves significant risks, including counterparty risk and market risk. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Regulations like Dodd-Frank impact CDS trading, requiring transparency and stricter oversight. |
| Pricing & Valuation | CDS pricing depends on several factors including credit rating, maturity, and market sentiment. |
Let's dive deeper into the key aspects of buying credit default swaps, starting with the foundational principles and moving on to the practical aspects of execution.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Buying CDS
-
Understanding the Contract: A CDS is a contract where the protection buyer (investor) makes periodic payments (premiums) to the protection seller (usually an institution) until either the contract matures or the reference entity defaults. If a credit event (like default) occurs before maturity, the protection seller compensates the buyer for the loss. The contract specifies the notional principal, the spread (premium), the maturity date, and the definition of a credit event.
-
Accessing the Market: Buying CDS contracts requires access to the over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives market. This typically involves establishing relationships with major investment banks or brokerage firms specializing in fixed income and derivatives trading. These institutions act as intermediaries, facilitating the trade execution and providing access to market pricing. Investors need substantial capital and a thorough understanding of the market to participate.
-
Determining the Underlying Asset: The first step is identifying the specific debt instrument whose credit risk you wish to hedge or speculate on. This could be a corporate bond, a bank loan, or even a sovereign debt. Thorough credit analysis of the reference entity is crucial. Factors to consider include the company's financial statements, industry position, management quality, and overall economic outlook.
-
Selecting a CDS Contract: Once the underlying asset is chosen, the next step is choosing the appropriate CDS contract. This involves considering the notional principal (the amount of protection), the maturity date (the length of the contract), and the spread (the periodic premium payment). The spread reflects the perceived credit risk of the underlying asset – higher risk implies a higher spread.
-
Negotiating the Trade: Unlike exchange-traded instruments, CDS trades are negotiated bilaterally between the buyer and seller. This involves negotiating the terms of the contract, including the spread, maturity, and the definition of a credit event. This negotiation often happens through electronic platforms and involves sophisticated pricing models.
-
Executing the Trade: Once terms are agreed upon, the trade is executed through the chosen intermediary (investment bank or brokerage). The trade confirmation details all the specifics of the contract. Post-trade processes include clearing and settlement of the contract, usually through a clearinghouse to mitigate counterparty risk.
Closing Insights
Buying credit default swaps involves navigating a complex market with significant risks and rewards. It's essential to have a solid understanding of credit analysis, market dynamics, and regulatory requirements. Effective risk management is paramount, and only sophisticated investors with appropriate resources and expertise should participate. The ability to accurately assess credit risk and manage exposure is crucial for success in the CDS market.
Exploring the Connection Between Counterparty Risk and CDS
Counterparty risk, the risk that the other party in a financial contract will default, is a significant concern in the CDS market. Because CDS trades are OTC contracts, the risk that the protection seller might fail to make payments in the event of a credit event is substantial. This risk is particularly pronounced during periods of market stress when financial institutions are under pressure.
Roles and Real-World Examples: Imagine a large financial institution selling CDS protection. If this institution experiences financial difficulties, it may be unable to fulfill its obligations to the CDS buyer, even if the reference entity defaults. The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the systemic risk associated with counterparty defaults in the CDS market.
Risks and Mitigations: Several mechanisms are employed to mitigate counterparty risk, including:
- Central Clearing: Increasingly, CDS trades are being cleared through central counterparties (CCPs), which act as intermediaries, reducing the risk of a bilateral default.
- Collateralization: Some CDS contracts require collateralization, ensuring that the protection seller has sufficient funds to meet its obligations.
- Credit Rating Assessments: Investors carefully assess the creditworthiness of the protection seller before entering into a CDS contract.
Impact and Implications: Counterparty defaults in the CDS market can have significant cascading effects, potentially leading to further market instability. The systemic risk associated with counterparty risk underscores the importance of robust regulatory oversight and risk management practices in the CDS market.
Further Analysis of Counterparty Risk
| Factor | Cause & Effect | Significance | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Health of Seller | Poor financial health increases the likelihood of default. | Directly impacts the ability of the seller to fulfill its obligations. | Due diligence, credit rating checks, and collateralization are essential risk mitigation strategies. |
| Market Volatility | Increased market uncertainty increases default risk for financial institutions. | Heightened uncertainty creates more risk for CDS buyers. | Diversification of CDS exposures and adjusting positions based on market conditions are important. |
| Regulatory Environment | Changes in regulations can impact the financial strength of institutions and their ability to meet obligations. | Affects the risk profile of CDS sellers. | Staying informed about regulatory changes and their potential implications is critical. |
| Liquidity Conditions | Tight liquidity in the financial system increases the difficulty of meeting payment obligations. | Exacerbates the counterparty risk in CDS transactions. | Monitoring market liquidity conditions and adjusting trading strategies accordingly are important measures. |
FAQ Section
-
What is the minimum investment to buy a CDS? There's no fixed minimum; it depends on the notional principal of the contract and the broker's requirements. Generally, it's a significant investment, typically accessible only to institutional investors.
-
How are CDS premiums paid? CDS premiums are typically paid quarterly in arrears.
-
What constitutes a credit event triggering a payout? The definition of a credit event is clearly specified in the contract and usually includes bankruptcy, failure to pay, or restructuring.
-
Are CDS contracts standardized? No, they are typically customized OTC contracts, making it essential to understand each contract's specific terms.
-
How are CDS contracts valued? CDS valuation is complex and relies on credit spreads, risk-free rates, and market models.
-
What are the tax implications of CDS trading? Tax implications vary by jurisdiction and depend on the nature of the transaction and the investor's tax status. Seeking professional tax advice is crucial.
Practical Tips
- Conduct thorough due diligence: Before buying a CDS, perform a comprehensive credit analysis of both the reference entity and the protection seller.
- Diversify CDS exposures: Avoid concentrating CDS purchases on a single reference entity or sector.
- Monitor market conditions: Keep a close eye on market developments that could impact the creditworthiness of the reference entity or the protection seller.
- Use appropriate risk management techniques: Employ strategies such as hedging and diversification to manage the risks associated with CDS trading.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with financial advisors and legal professionals specializing in derivatives to ensure compliance with regulations and understand the complexities of CDS contracts.
- Understand the terms of the contract: Carefully review the terms and conditions of the CDS contract before entering into the agreement.
- Use reputable intermediaries: Work only with established and reputable investment banks and brokerage firms when trading CDS.
- Maintain accurate records: Maintain detailed records of all CDS transactions, including contract terms and payment schedules.
Final Conclusion
Credit Default Swaps (CDS) are sophisticated financial instruments offering a powerful tool for managing credit risk, but their complexity requires careful consideration. Successful participation necessitates thorough due diligence, prudent risk management, and a deep understanding of market dynamics and regulatory compliance. By adhering to best practices and seeking professional guidance, investors can leverage the benefits of the CDS market while effectively managing the associated risks. The information provided in this article is intended for educational purposes and should not be considered financial advice. Always seek professional guidance before making investment decisions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
New Indications Definition
Apr 01, 2025
-
New Home Sales Definition
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is New Growth Theory Definition How Its Used And Example
Apr 01, 2025
-
New Fund Offer Nfo Definition Types Launches And Benefits
Apr 01, 2025
-
New Economy Definition History Examples Of Companies
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Buy Credit Default Swaps . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.