Purchase To Pay P2p Definition Process Steps And Benefits
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
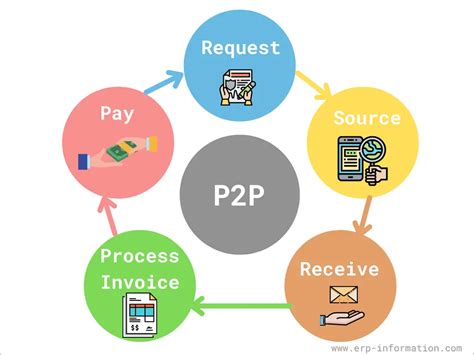
Table of Contents
Unlocking Efficiency: A Deep Dive into Purchase-to-Pay (P2P) Processes
What are the hidden costs lurking within your procurement process?
A streamlined Purchase-to-Pay (P2P) system can dramatically reduce expenses, improve accuracy, and enhance overall financial control.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to Purchase-to-Pay (P2P) processes has been published today to provide businesses with the latest insights and best practices.
Why Purchase-to-Pay (P2P) Matters
In today's fast-paced business environment, efficient and effective procurement is paramount. The Purchase-to-Pay (P2P) process, encompassing all stages from initial purchase requisition to final payment, is the backbone of a company's financial health. A poorly managed P2P process can lead to significant inefficiencies, increased costs, delayed payments, and even compliance issues. Conversely, a well-optimized P2P system offers substantial benefits, including improved cash flow, reduced operational costs, and enhanced supplier relationships. Understanding the intricacies of P2P is crucial for businesses of all sizes seeking to optimize their financial operations and gain a competitive edge. This impacts not just the finance department, but also procurement, accounts payable, and even operational teams reliant on timely material acquisition.
Overview of this Article
This article provides a detailed examination of the Purchase-to-Pay process, exploring its key stages, associated benefits, and potential challenges. We will delve into the definition of P2P, outline the crucial steps involved, and discuss how technology is transforming this critical business function. Readers will gain a clear understanding of how to implement and optimize a P2P system to achieve greater efficiency and control over their financial processes. The article concludes with practical tips and best practices for maximizing the return on investment from a robust P2P strategy.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The insights presented in this article are based on extensive research, incorporating industry best practices, case studies from various sectors, and analysis of leading P2P software solutions. We have drawn upon data from reputable sources, including industry reports and expert opinions, to ensure accuracy and relevance. The information provided aims to be a practical guide for businesses seeking to improve their procurement and payment processes.
Key Takeaways
| Key Area | Insight |
|---|---|
| P2P Definition | Encompasses all stages from requisition to payment, aiming for efficiency and control. |
| Process Steps | Requisition, Purchase Order, Goods Receipt, Invoice Processing, Payment. |
| Automation Benefits | Reduced errors, improved efficiency, faster processing times, enhanced visibility, better cash flow. |
| Integration & Visibility | Seamless data flow between systems improves accuracy and reduces manual intervention. |
| Risk Mitigation | Improved controls, fraud prevention, compliance adherence. |
| Supplier Relationship | Streamlined communication and payment improves supplier satisfaction and collaboration. |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Now, let’s delve into the core aspects of Purchase-to-Pay, starting with a precise definition and then progressing through each key step in the process.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Purchase-to-Pay
1. Defining Purchase-to-Pay (P2P): Purchase-to-Pay (P2P) is a comprehensive business process that manages the entire lifecycle of a purchase, from the initial request for goods or services to the final payment to the supplier. This encompasses all activities related to procuring, receiving, and paying for goods and services. A successful P2P process streamlines these activities, minimizing manual intervention, reducing errors, and improving overall efficiency.
2. The P2P Process Steps: The typical P2P process involves several key steps:
-
Requisition: This is the initial stage where a department or individual identifies a need for goods or services and submits a formal requisition. This often involves specifying the required items, quantities, and desired delivery date. Modern systems often use electronic requisition forms, integrating directly with inventory management or other systems.
-
Purchase Order (PO) Creation: Based on the approved requisition, a purchase order is generated. This serves as a legally binding document outlining the terms and conditions of the purchase, including item details, pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedule. POs are crucial for tracking orders and managing vendor relationships.
-
Goods Receipt/Service Acceptance: Upon delivery of goods or completion of services, a goods receipt or service acceptance note is generated. This confirms receipt of the ordered items and verifies their conformity to the purchase order. Discrepancies are identified and addressed at this stage.
-
Invoice Processing: The supplier submits an invoice for the goods or services provided. This invoice is then matched against the purchase order and goods receipt/service acceptance documents (the "three-way match"). This crucial step verifies the accuracy of the invoice and prevents payment for unordered or incorrect goods/services.
-
Payment: Once the invoice is verified, the payment is processed and released to the supplier. This may involve various payment methods, including electronic funds transfer (EFT), checks, or credit card payments. Efficient P2P systems often automate this process.
3. Automation in P2P: Automation is revolutionizing the P2P process, offering significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy. Automated P2P systems leverage technologies such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and machine learning to streamline various aspects of the process. This includes automated invoice processing, purchase order generation, and payment approvals.
4. The Role of Technology in P2P: Software solutions specifically designed for P2P management play a critical role in optimizing the entire process. These systems often integrate with existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, providing a centralized platform for managing all aspects of procurement and payment. Cloud-based P2P solutions offer scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt to changing needs.
5. Benefits of a Robust P2P System: The advantages of a well-implemented P2P system are substantial and extend beyond mere cost savings. They include:
- Reduced Processing Costs: Automating manual tasks significantly reduces labor costs associated with invoice processing, purchase order management, and payment processing.
- Improved Accuracy: Automation minimizes human error, leading to more accurate data and reduced discrepancies.
- Enhanced Visibility and Control: Real-time visibility into all aspects of the P2P process allows for better monitoring and control of spending.
- Faster Payment Cycles: Streamlined processes lead to quicker invoice processing and payment, improving supplier relationships and cash flow.
- Improved Cash Flow Management: Predictable payment cycles improve cash flow forecasting and planning.
- Stronger Supplier Relationships: Timely payments and clear communication foster strong supplier relationships, securing favorable terms and reliable supply chains.
- Enhanced Compliance: Automated systems ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, minimizing the risk of penalties.
- Reduced Fraud Risk: Robust controls and audit trails reduce the risk of fraudulent activities.
Exploring the Connection Between Data Analytics and Purchase-to-Pay
Data analytics plays a crucial role in optimizing the P2P process. By analyzing data from various stages of the P2P cycle, businesses can identify areas for improvement, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency. This includes analyzing invoice processing times, identifying bottlenecks, and tracking spending patterns to uncover potential cost savings. For example, analyzing historical data on supplier performance can reveal opportunities to negotiate better pricing or consolidate suppliers. Predictive analytics can forecast future spending needs, allowing businesses to optimize inventory management and avoid stockouts or overstocking.
Further Analysis of Data Analytics in P2P:
| Analytical Approach | Application in P2P | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Descriptive Analytics | Analyzing historical P2P data to identify trends and patterns. | Understanding past performance, identifying bottlenecks. |
| Diagnostic Analytics | Investigating the root causes of delays or inefficiencies in the P2P process. | Pinpointing areas for improvement, process optimization. |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasting future spending needs based on historical data and market trends. | Optimizing inventory, improving cash flow forecasting. |
| Prescriptive Analytics | Recommending actions to optimize the P2P process and improve efficiency. | Automated decision-making, proactive problem-solving. |
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the difference between P2P and Procure-to-Pay (PTP)? While often used interchangeably, PTP is a broader term encompassing the entire procurement process, including sourcing, contract negotiation, and supplier management, whereas P2P focuses specifically on the transactional aspects from purchase requisition to payment.
Q2: How can I implement a P2P system effectively? Start by identifying your current pain points and setting clear goals. Choose a P2P solution that aligns with your business needs and integrates with existing systems. Provide adequate training to your staff, and monitor the system closely to identify areas for improvement.
Q3: What are the common challenges in P2P processes? Common challenges include manual processes, data silos, lack of visibility, invoice processing errors, and poor supplier relationships.
Q4: How can I improve supplier relationships with a better P2P system? A streamlined P2P system ensures timely payments, clear communication, and efficient dispute resolution, fostering stronger relationships.
Q5: What are the key metrics for measuring P2P performance? Key metrics include invoice processing time, payment cycle time, invoice error rate, and cost per invoice.
Q6: Is cloud-based P2P software a good option? Cloud-based P2P solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, making them a suitable option for many businesses.
Practical Tips for Optimizing Your P2P Process
-
Automate wherever possible: Implement automation for tasks like invoice processing, purchase order generation, and payment approvals.
-
Improve data visibility: Gain real-time visibility into all aspects of the P2P process through a centralized system.
-
Streamline invoice processing: Use electronic invoicing and optical character recognition (OCR) to automate invoice data entry.
-
Implement a three-way match: Match purchase orders, goods receipts, and invoices to ensure accuracy and prevent errors.
-
Negotiate favorable payment terms with suppliers: Collaborate with suppliers to agree on favorable payment terms that optimize your cash flow.
-
Establish clear roles and responsibilities: Define clear roles and responsibilities for each stage of the P2P process.
-
Regularly review and optimize your P2P process: Continuously monitor and analyze your P2P performance to identify areas for improvement.
-
Invest in training and development: Provide adequate training to your staff on the P2P system and processes.
Final Conclusion
Purchase-to-Pay is more than just a set of processes; it's a strategic function that significantly impacts a company's financial health and operational efficiency. By understanding the key steps, benefits, and challenges associated with P2P, businesses can implement effective strategies to optimize their procurement and payment processes. Investing in a robust P2P system and leveraging the power of data analytics are crucial steps towards achieving greater efficiency, reducing costs, and strengthening supplier relationships. The journey towards a streamlined P2P system requires a proactive and data-driven approach, focusing on continuous improvement and leveraging the latest technological advancements. The rewards, however, are undeniable – a more efficient, controlled, and profitable business operation.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Purchase To Pay P2p Definition Process Steps And Benefits . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.