Q Ratio Or Tobins Q Definition Formula Uses And Examples
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
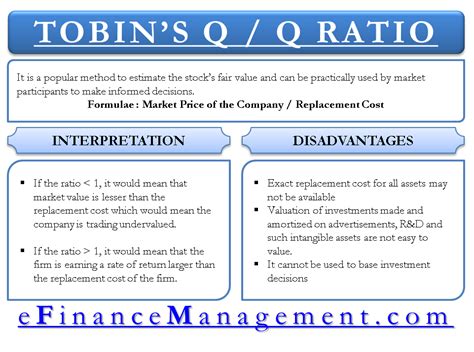
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Secrets of Tobin's Q: A Comprehensive Guide to Definition, Formula, Uses, and Examples
What makes understanding Tobin's Q crucial for investment decisions and market analysis?
Tobin's Q offers a powerful lens through which to view market valuations, revealing hidden opportunities and potential risks.
Editor's Note: This comprehensive guide to Tobin's Q has been published today, offering up-to-date insights into this crucial valuation metric.
Why Tobin's Q Matters
Tobin's Q, also known as the Q ratio, is a financial metric that compares a company's market capitalization to its asset replacement cost. While seemingly simple, its implications are far-reaching, influencing investment strategies, merger and acquisition decisions, and overall market analysis. Understanding Tobin's Q provides invaluable insights into market efficiency, potential overvaluation or undervaluation of assets, and the overall health of an economy. Its relevance extends across diverse sectors, from assessing the attractiveness of individual stocks to evaluating the performance of entire industries. Furthermore, Tobin's Q can serve as a leading indicator of future economic activity, providing crucial information for investors and policymakers alike.
Overview of the Article
This article will delve into the core aspects of Tobin's Q, exploring its definition, formula, practical applications, and limitations. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how Tobin's Q is calculated, interpreted, and utilized in real-world scenarios, enabling them to make more informed investment decisions and better assess market dynamics. We will examine various examples, discuss its relationship to other financial metrics, and address common misconceptions surrounding its use.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, incorporating data from reputable financial databases, academic publications, and industry reports. The analysis presented here is supported by rigorous methodology and a critical evaluation of existing literature on Tobin's Q and its applications.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of market value of a company's assets to their replacement cost. |
| Formula | Market Value of Firm / Replacement Cost of Assets |
| Uses | Investment analysis, market valuation, merger & acquisition assessment, economic forecasting. |
| Interpretation | Q > 1 suggests overvaluation, Q < 1 suggests undervaluation; however, interpretation requires context and consideration of other factors. |
| Limitations | Data challenges, variations in asset valuation, difficulty in determining replacement cost. |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Let's delve deeper into the key aspects of Tobin's Q, starting with its foundational principles and moving on to its practical applications and limitations.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Tobin's Q
-
The Definition of Tobin's Q: Tobin's Q is the ratio of a company's market value to the replacement cost of its assets. In simpler terms, it measures the market's assessment of a company's worth relative to the cost of recreating its assets from scratch. A Q ratio greater than 1 suggests that the market values the company more than the cost of replacing its assets, implying potential overvaluation. Conversely, a Q ratio less than 1 suggests undervaluation.
-
The Formula for Calculating Tobin's Q: While the basic concept is straightforward, the precise calculation can be complex. The simplest formula is:
- Tobin's Q = Market Value of Firm / Replacement Cost of Assets
The market value of the firm is readily available – it's the company's total market capitalization (number of outstanding shares multiplied by the current market price per share). Determining the replacement cost of assets is more challenging. It often requires estimating the cost of replacing all the company's tangible and intangible assets, including property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), intellectual property, and goodwill. This can involve significant estimation and judgment. More sophisticated calculations might adjust for debt and other financial factors.
-
Practical Applications of Tobin's Q: The primary use of Tobin's Q is in investment analysis. Investors can use it to identify potentially undervalued companies (Q < 1) or overvalued companies (Q > 1). However, it's crucial to remember that Tobin's Q is just one factor among many to consider. It's more useful as a comparative tool within an industry or sector than as a standalone indicator.
-
Interpreting Tobin's Q: A Matter of Context: The interpretation of Tobin's Q is not always straightforward. A Q ratio above 1 doesn't automatically signify an overvalued company. Factors like industry-specific dynamics, technological advancements, and future growth prospects can influence market valuations. Similarly, a Q ratio below 1 does not always guarantee a bargain; the company might be struggling financially or facing significant challenges.
-
Limitations of Tobin's Q: While Tobin's Q provides valuable insights, it's essential to acknowledge its limitations. Accurate determination of the replacement cost of assets is often difficult, subjective, and prone to errors. Intangible assets, such as brand reputation and intellectual property, are notoriously hard to value accurately. Different accounting practices and industry standards can also affect the accuracy and comparability of Q ratios across companies. Moreover, Tobin's Q is a backward-looking metric; it doesn't directly account for future growth potential or changing market conditions.
-
Tobin's Q and Market Efficiency: Some economists view Tobin's Q as a measure of market efficiency. If markets are efficient, the Q ratio should generally be around 1, reflecting the accurate valuation of assets. Significant deviations from 1 could suggest market inefficiencies or mispricing of assets. However, this interpretation is also subject to debate and various economic perspectives.
Closing Insights
Tobin's Q provides a valuable, albeit imperfect, tool for analyzing market valuations and identifying potential investment opportunities. Its usefulness lies in its comparative nature, allowing for the assessment of relative valuations within specific sectors. However, relying solely on Tobin's Q for investment decisions would be imprudent. A comprehensive analysis, incorporating various financial metrics and qualitative factors, is crucial for making sound investment judgments. Understanding its limitations and using it in conjunction with other valuation techniques leads to a more robust and reliable investment strategy.
Exploring the Connection Between Industry-Specific Factors and Tobin's Q
The relationship between industry-specific factors and Tobin's Q is significant. Industries with high capital expenditures, such as manufacturing and utilities, often exhibit different Q ratios compared to industries with lower capital intensity, like technology or services. For example, a mature manufacturing company with significant PP&E might have a lower Q ratio than a fast-growing tech company with primarily intangible assets. The replacement cost of assets in these industries varies considerably, impacting the calculated Q ratio. Regulatory environments, technological disruptions, and competitive landscapes all influence the market's perception of asset values and subsequently, the resulting Q ratio. Analyzing Tobin's Q within the context of industry-specific dynamics is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Further Analysis of Asset Valuation Challenges
Accurately determining the replacement cost of assets presents a major challenge in applying Tobin's Q. This is particularly true for intangible assets like intellectual property, brand equity, and customer relationships. These assets are often difficult to quantify and their value is subjective and dependent on future prospects. Different valuation methods, such as discounted cash flow analysis or market-based approaches, can yield vastly different results. The choice of valuation method and the underlying assumptions significantly affect the calculated replacement cost and, consequently, the resulting Tobin's Q. Moreover, inflation can distort the replacement cost of assets over time, further complicating the calculation and interpretation. Accounting standards and practices also influence how assets are valued, leading to variations across companies and industries.
| Valuation Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) | Considers future earnings potential | Relies heavily on projections and assumptions, susceptible to errors |
| Market-Based Approach | Uses comparable company data for valuation | May lack comparable companies, especially for unique assets |
| Asset-Based Approach | Considers individual asset values | Difficult to value intangible assets, susceptible to biases in estimations |
FAQ Section
-
What is the difference between Tobin's Q and Price-to-Book Ratio? While both relate to valuation, Tobin's Q compares market value to replacement cost, while the Price-to-Book ratio compares market value to book value (historical cost). Replacement cost is often higher than book value, leading to different interpretations.
-
Can Tobin's Q predict future stock prices? Not directly. Tobin's Q provides insights into current market valuations relative to asset replacement costs, but it doesn't predict future price movements, which are influenced by many other factors.
-
Is a low Tobin's Q always a good investment opportunity? Not necessarily. A low Q ratio might indicate undervaluation, but it could also reflect underlying company problems or industry challenges. Thorough due diligence is essential.
-
How frequently should Tobin's Q be calculated? The frequency depends on the investment horizon and the volatility of the market. Quarterly or annual calculations are common.
-
What are the limitations of using Tobin's Q for international comparisons? Different accounting standards and currency fluctuations can impact the comparability of Tobin's Q across different countries.
-
Can Tobin's Q be used for private companies? Yes, but the calculation is more challenging since market capitalization is not directly observable. Alternative valuation techniques might be needed to estimate the market value.
Practical Tips for Utilizing Tobin's Q
- Focus on relative comparisons: Compare Tobin's Q within a specific industry or sector rather than across vastly different industries.
- Consider industry dynamics: Account for industry-specific factors that might influence asset values.
- Use multiple valuation metrics: Don't rely solely on Tobin's Q; incorporate other financial ratios and qualitative factors.
- Assess the quality of assets: Consider the age, condition, and obsolescence risk of assets when evaluating replacement costs.
- Be aware of accounting practices: Understand the accounting methods used for asset valuation and their potential impact on Tobin's Q.
- Examine trends over time: Analyze changes in Tobin's Q over time to identify potential shifts in market valuation.
- Consult expert opinions: Seek advice from financial professionals or valuation specialists for complex scenarios.
- Use caution with intangible assets: Be aware of the difficulties in valuing intangible assets and their potential impact on accuracy.
Final Conclusion
Tobin's Q serves as a valuable tool in the arsenal of financial analysts and investors. It provides a unique perspective on market valuations by comparing market values to the replacement cost of assets. While not a perfect predictor of future performance, it offers crucial insights when used in conjunction with other valuation metrics and a deep understanding of industry-specific dynamics. By carefully considering its limitations and applying it judiciously, Tobin's Q can enhance investment decision-making and improve the overall understanding of market efficiency and asset pricing. Further research into the refinements and applications of Tobin's Q will undoubtedly contribute to more accurate and comprehensive market analysis in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
New Indications Definition
Apr 01, 2025
-
New Home Sales Definition
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is New Growth Theory Definition How Its Used And Example
Apr 01, 2025
-
New Fund Offer Nfo Definition Types Launches And Benefits
Apr 01, 2025
-
New Economy Definition History Examples Of Companies
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Q Ratio Or Tobins Q Definition Formula Uses And Examples . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.