Rebate Barrier Option Definition
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 10 min read
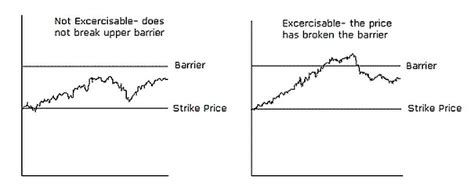
Table of Contents
Rebate Barrier Option: Unveiling the Hidden Power of Contingent Payments
What truly distinguishes a rebate barrier option from other exotic options?
Rebate barrier options offer a unique blend of risk management and potential profit, making them a powerful tool for sophisticated investors.
Editor’s Note: The definition and intricacies of Rebate Barrier Options have been updated today.
Why Rebate Barrier Options Matter
Rebate barrier options are not your typical vanilla options. They represent a sophisticated class of exotic options that offer a unique blend of risk management and profit potential. Unlike standard options, which expire worthless if the underlying asset doesn't reach a specific strike price, rebate barrier options provide a predetermined payment if the barrier is breached, regardless of the option's final value. This feature makes them attractive to investors seeking to hedge against downside risk while still participating in potential upside gains. Their importance lies in their ability to tailor risk profiles to specific investment strategies and market conditions. They are particularly relevant in volatile markets where the potential for sharp price movements is high, offering a safety net against adverse events. The use of rebate barrier options has increased across various asset classes, from equities and commodities to currencies and interest rates, highlighting their growing importance in the financial landscape.
Overview of the Article
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of rebate barrier options. It delves into their definition, different types, pricing models, applications, and risk management aspects. Readers will gain a deeper understanding of how these options function, their advantages and disadvantages, and practical strategies for their effective utilization. The article also examines the relationship between rebate barrier options and other financial instruments, exploring their potential to enhance portfolio diversification and risk mitigation. Finally, frequently asked questions are answered, and actionable tips are provided to assist readers in applying this knowledge.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The insights presented in this article are based on extensive research, drawing upon academic literature, industry publications, and practical experience in derivatives trading. The analysis incorporates established option pricing models and explores real-world examples to illustrate the practical implications of rebate barrier options. Data from reputable sources has been used to support the claims made throughout the article, ensuring accuracy and credibility.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A contingent claim offering a predetermined payment if a pre-defined barrier is breached, regardless of expiry. |
| Types | Up-and-out, down-and-out, up-and-in, down-and-in, with variations in rebate structures. |
| Pricing | Complex; relies on numerical methods (e.g., finite difference, Monte Carlo simulation) due to path dependency. |
| Applications | Hedging downside risk, speculation on price movements, portfolio optimization. |
| Risk Management | Offers a safety net but doesn't eliminate risk entirely; careful consideration of barrier levels is crucial. |
Let’s delve deeper into the key aspects of rebate barrier options, beginning with a clear definition and exploration of its different variations.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Rebate Barrier Options
-
Defining Rebate Barrier Options: A rebate barrier option is a path-dependent option contract that provides a specified rebate payment to the option holder if the underlying asset's price reaches a predetermined barrier level (the barrier) before the option's expiration date. This rebate is paid regardless of whether the option finishes in-the-money or out-of-the-money. The option may or may not continue to exist after the barrier is triggered, depending on whether it's a "knock-out" or "knock-in" type.
-
Types of Rebate Barrier Options: Several variations exist, categorized primarily by whether the barrier triggers a knock-out (option ceases to exist) or a knock-in (option comes into existence only if the barrier is hit) event.
-
Down-and-Out Rebate Option: This option ceases to exist if the underlying asset price falls below a specified lower barrier. If the barrier is hit, the holder receives the rebate and the option expires worthless.
-
Up-and-Out Rebate Option: This option ceases to exist if the underlying asset price rises above a specified upper barrier. If the barrier is hit, the holder receives the rebate, and the option expires worthless.
-
Down-and-In Rebate Option: This option only comes into existence if the underlying asset price falls below a specified lower barrier before the option's expiration date. If the barrier is not hit, the option expires worthless. If the barrier is hit, the option becomes active and behaves like a standard option, with the rebate added.
-
Up-and-In Rebate Option: This option only comes into existence if the underlying asset price rises above a specified upper barrier before the option's expiration date. If the barrier is not hit, the option expires worthless. If the barrier is hit, the option becomes active and behaves like a standard option, with the rebate added.
Each type offers a distinct risk-reward profile, allowing investors to tailor their exposure to specific market scenarios.
-
-
Pricing Rebate Barrier Options: Pricing these options is considerably more complex than pricing standard options due to their path-dependency. Simple closed-form solutions do not exist. Instead, sophisticated numerical methods are typically employed:
-
Monte Carlo Simulation: This method simulates numerous price paths of the underlying asset, allowing for the calculation of the expected payoff and, consequently, the option's price.
-
Finite Difference Methods: These methods discretize the option pricing partial differential equation and solve it numerically, providing an approximation of the option's value.
These methods require substantial computational power and input parameters, including the volatility of the underlying asset, the risk-free interest rate, the dividend yield (if applicable), and the time to maturity.
-
-
Applications of Rebate Barrier Options: The versatility of rebate barrier options leads to various applications:
-
Risk Management: These options can be used to hedge against significant downside risk. For example, a portfolio manager concerned about a sharp decline in a particular stock could buy a down-and-out rebate option to protect against substantial losses while still retaining some upside potential.
-
Speculation: Rebate barrier options can also be used for speculative purposes. For instance, an investor might buy an up-and-in rebate option if they believe the price of an asset will break through a certain resistance level, allowing them to profit from the subsequent price rise.
-
Portfolio Optimization: By carefully selecting the type, barrier level, and rebate amount, investors can construct strategies that optimize their portfolio's risk-reward profile.
-
-
Risk Management Considerations: While rebate barrier options offer a safety net, it is crucial to understand their limitations:
-
Barrier Level Selection: The choice of barrier level is critical. Setting it too high or too low could significantly impact the option's payoff.
-
Rebate Amount: The rebate amount needs careful consideration. A small rebate might not adequately compensate for the loss of the option, while a large rebate could make the option too expensive.
-
Underlying Asset Volatility: The volatility of the underlying asset directly influences the option's price and the likelihood of the barrier being breached.
-
Closing Insights
Rebate barrier options provide a sophisticated tool for managing risk and capturing opportunities in volatile markets. Their path-dependent nature and contingent rebate payment structure offer a unique blend of protection and participation in potential gains. However, careful consideration of the barrier level, rebate amount, and underlying asset volatility is crucial for successful implementation. Their application extends across diverse asset classes, making them a valuable instrument for both risk-averse and risk-seeking investors.
Exploring the Connection Between Volatility and Rebate Barrier Options
Volatility plays a pivotal role in determining the price and effectiveness of rebate barrier options. High volatility increases the probability of the barrier being breached, making down-and-out options more expensive (because of the higher probability of the rebate being paid) and up-and-in options less expensive (because the barrier is more likely to be hit). Conversely, low volatility decreases the likelihood of the barrier being breached. The impact of volatility is further amplified by the time to maturity; longer maturities generally increase the probability of barrier breach.
Further Analysis of Volatility's Impact
The following table summarizes the effects of different volatility levels on rebate barrier options:
| Volatility Level | Down-and-Out Rebate Option | Up-and-In Rebate Option |
|---|---|---|
| High Volatility | Higher Price (higher probability of rebate payout) | Lower Price (higher probability of barrier breach) |
| Low Volatility | Lower Price (lower probability of rebate payout) | Higher Price (lower probability of barrier breach) |
This relationship highlights the importance of accurate volatility forecasting when pricing and trading these options. Models that incorporate stochastic volatility (volatility that changes over time) are often preferred for more accurate pricing.
FAQ Section
-
Q: What is the main advantage of a rebate barrier option over a standard option? A: The main advantage is the built-in protection. If the barrier is breached, the investor receives a rebate, mitigating some of the downside risk.
-
Q: How are rebate barrier options priced? A: Due to their path dependency, closed-form solutions are unavailable. Numerical methods like Monte Carlo simulation or finite difference methods are used.
-
Q: What factors influence the price of a rebate barrier option? A: Volatility of the underlying asset, time to maturity, risk-free interest rate, barrier level, and rebate amount are key factors.
-
Q: Are rebate barrier options suitable for all investors? A: No. They are more suitable for sophisticated investors with a good understanding of derivatives and risk management.
-
Q: What are the risks associated with rebate barrier options? A: Incorrect barrier level selection, inaccurate volatility estimations, and the possibility of the option becoming worthless before the barrier is breached are all risks.
-
Q: How can I learn more about trading rebate barrier options? A: Consult financial literature, take advanced derivatives courses, or seek guidance from experienced financial professionals.
Practical Tips
-
Understand the Underlying Asset: Thoroughly research the underlying asset's characteristics, including its historical volatility and price trends.
-
Carefully Select the Barrier Level: Choose a barrier level that aligns with your risk tolerance and market outlook.
-
Consider the Rebate Amount: The rebate should be sufficient to compensate for potential losses.
-
Use Appropriate Pricing Models: Employ sophisticated pricing models that account for the option's path-dependent nature and volatility.
-
Monitor Market Conditions: Keep a close eye on market developments and adjust your strategy accordingly.
-
Diversify Your Portfolio: Don't rely solely on rebate barrier options for risk management. Diversification is key.
-
Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor before investing in these complex instruments.
-
Practice with Simulations: Before using real capital, practice trading strategies using simulations or paper trading accounts.
Final Conclusion
Rebate barrier options represent a powerful tool within a sophisticated investor's arsenal. Their ability to offer a customized blend of risk management and profit potential distinguishes them from standard options. However, their complexity demands a thorough understanding of their mechanics, pricing, and risk implications. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this article and employing sound risk management practices, investors can leverage these options to effectively manage risk and pursue potentially lucrative trading opportunities. Further exploration into the nuances of option pricing models and risk mitigation strategies will enhance the effectiveness of using these instruments. The key to success lies in thorough research, careful planning, and a disciplined approach to trading.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rebate Barrier Option Definition . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.