What Are Hedging Costs
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 8 min read
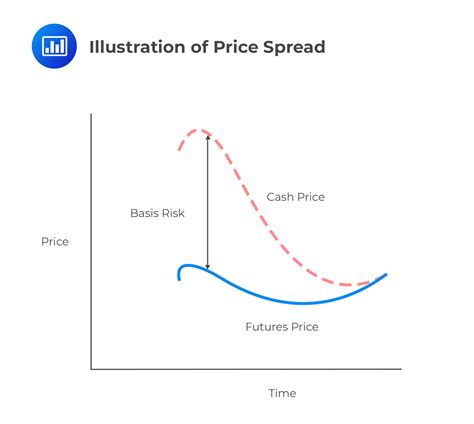
Table of Contents
Uncovering the Hidden Costs of Hedging: A Comprehensive Guide
What are hedging costs, and why should businesses care?
Hedging costs, often unseen but always present, significantly impact a company's profitability and strategic decision-making. Understanding these costs is crucial for effective risk management.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to hedging costs was published today, offering the latest insights and analysis for businesses navigating financial uncertainty.
Why Hedging Costs Matter
Hedging, the process of mitigating financial risk associated with price fluctuations of assets like commodities, currencies, or interest rates, is a cornerstone of modern financial strategy. While the primary goal is risk reduction, hedging inevitably incurs costs. Understanding these costs is critical because they represent the price of financial security. Overlooking them can lead to inaccurate financial projections, flawed risk assessments, and ultimately, suboptimal business decisions. These costs are especially relevant in industries highly exposed to commodity price volatility, fluctuating exchange rates, or interest rate shifts, such as agriculture, manufacturing, energy, and international trade.
Overview of this Article
This article provides a detailed exploration of hedging costs, covering their various components, influencing factors, and methods for analysis and optimization. We will examine different hedging strategies, explore the relationship between hedging costs and effectiveness, and offer practical advice for businesses seeking to manage these costs effectively. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the financial implications of hedging and develop a more sophisticated approach to risk management.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The insights presented here are based on extensive research, drawing upon academic literature on financial risk management, industry reports on hedging practices, and real-world examples from various sectors. The analysis employs a framework that considers both the explicit and implicit costs associated with hedging, providing a holistic perspective.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Explicit Costs | Directly observable and measurable, including transaction fees, commissions, and premiums. |
| Implicit Costs | Indirect and less tangible, encompassing opportunity costs, basis risk, and potential losses from imperfect hedges. |
| Impact of Hedging Strategy | Different strategies (futures, options, swaps) incur varying costs and offer different levels of risk protection. |
| Cost Optimization | Techniques for minimizing hedging costs while maintaining an acceptable level of risk reduction are crucial. |
| Risk-Return Trade-off | The optimal hedging strategy balances the cost of protection against the potential benefits of risk reduction. |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Let’s delve into the specifics of hedging costs, starting with a breakdown of the various cost components involved.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Hedging Costs
-
Transaction Costs: These are the explicit costs directly associated with executing a hedging strategy. They include brokerage commissions, exchange fees, and clearinghouse fees. The magnitude of these costs depends on the volume and frequency of trades, the chosen instrument, and the market's liquidity.
-
Premium Costs (Options): When using options contracts for hedging, a premium must be paid to acquire the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specified price. The premium's size depends on factors like the underlying asset's volatility, the time until expiration, and the strike price.
-
Basis Risk: Basis risk refers to the difference between the price of the hedging instrument and the price of the asset being hedged. A perfect hedge eliminates basis risk, but it's rarely achievable in practice. A mismatch in the characteristics of the hedging instrument and the asset being hedged (e.g., differing delivery dates or locations) can lead to basis risk and potentially reduce the effectiveness of the hedge.
-
Opportunity Costs: Hedging often requires committing capital that could have been invested elsewhere. This represents an opportunity cost, representing the potential return forgone by not investing the funds. The size of this opportunity cost depends on prevailing interest rates and alternative investment opportunities.
-
Monitoring and Management Costs: Effective hedging requires ongoing monitoring and management. This includes tracking market conditions, adjusting hedge positions as needed, and staying informed about relevant regulations. These costs can be significant, especially for complex hedging strategies involving multiple instruments.
-
Model Risk: Hedging often involves using sophisticated financial models to estimate risks and determine optimal hedging strategies. The accuracy of these models is crucial, and errors can lead to significant financial losses. Model risk is an implicit cost that arises from the limitations and assumptions inherent in any model.
Closing Insights
Hedging costs are an intrinsic part of managing financial risk. While seemingly unavoidable, a careful understanding of the different cost components, the impact of various hedging strategies, and effective cost optimization techniques is critical. Businesses need to approach hedging as a strategic decision, weighing the cost of protection against the potential financial losses from unhedged exposure. The optimal approach requires a balanced perspective, recognizing that a perfect hedge is rarely achievable and focusing instead on minimizing costs while achieving an acceptable level of risk mitigation.
Exploring the Connection Between Market Volatility and Hedging Costs
Market volatility significantly influences hedging costs. In highly volatile markets, the premiums for options contracts increase, reflecting the higher risk associated with price fluctuations. Similarly, the cost of futures contracts can rise as market participants demand a larger premium for taking on price risk. This direct relationship between volatility and hedging costs underscores the crucial role of market forecasting in effective hedging strategies. Businesses operating in volatile markets should anticipate higher hedging costs and adjust their strategies accordingly, perhaps considering alternative hedging approaches or accepting a higher level of residual risk.
Further Analysis of Basis Risk
Basis risk is a critical component of hedging costs, often underestimated. It arises from a mismatch between the hedging instrument and the asset being hedged. For example, hedging a specific type of wheat using a broad wheat futures contract exposes the business to basis risk due to regional price differences or variations in wheat quality. Minimizing basis risk requires careful selection of hedging instruments with characteristics as close as possible to the asset being hedged. Techniques like cross-hedging (using a related but not identical asset for hedging) can be effective but must be carefully evaluated to balance risk reduction with the added basis risk. The following table illustrates the impact of basis risk on hedging effectiveness:
| Scenario | Basis Risk | Hedging Effectiveness | Cost Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perfect Hedge | Zero | High | Relatively low |
| Partial Hedge | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Ineffective Hedge | High | Low | High |
FAQ Section
-
Q: Are hedging costs tax-deductible? A: In many jurisdictions, hedging costs are tax-deductible, provided they are directly related to a business's risk management activities. However, specific rules and regulations vary by location, so consulting a tax professional is advisable.
-
Q: Can small businesses afford to hedge? A: Even small businesses can benefit from hedging, particularly if they are exposed to significant price volatility. While the costs may seem high initially, the potential savings from avoiding substantial losses can outweigh the hedging expenses.
-
Q: What is the difference between hedging and speculation? A: Hedging aims to reduce existing risk, whereas speculation involves taking on risk to potentially profit from market movements.
-
Q: How frequently should hedging strategies be reviewed? A: Hedging strategies should be reviewed regularly, typically on a quarterly or annual basis, to adjust for changing market conditions and business objectives.
-
Q: What happens if my hedge loses money? A: While hedging aims to reduce losses, there's always a possibility of incurring some losses. Properly structured hedges should limit potential losses to a manageable level.
-
Q: What are some alternative hedging strategies besides futures and options? A: Other hedging strategies include currency swaps, interest rate swaps, and forward contracts. The optimal choice depends on specific circumstances and risk profiles.
Practical Tips
-
Analyze Your Exposure: Thoroughly assess the extent of your exposure to price volatility, currency fluctuations, or interest rate risk.
-
Choose the Right Instruments: Select hedging instruments that closely match the characteristics of the assets being hedged to minimize basis risk.
-
Diversify Your Hedging Strategy: Don’t rely solely on one hedging instrument. A diversified approach can improve risk reduction and potentially reduce costs.
-
Monitor and Adjust Regularly: Continuously track market conditions and adjust your hedging positions as necessary.
-
Seek Professional Advice: Consult with financial professionals to develop and implement a robust hedging strategy tailored to your business's specific needs.
-
Negotiate Favorable Rates: Explore opportunities to negotiate lower transaction fees and commissions with brokers.
-
Consider Alternative Hedging Mechanisms: Explore options like insurance or risk-sharing agreements.
-
Document Your Hedging Strategy: Maintain detailed records of all hedging transactions and the rationale behind your decisions.
Final Conclusion
Hedging costs are an integral aspect of risk management, and understanding them is paramount for informed decision-making. While these costs represent the price of financial security, businesses can effectively manage and optimize them through careful planning, strategy selection, and diligent monitoring. By employing a balanced approach that considers the various cost components and potential benefits of risk reduction, businesses can integrate hedging into their overall financial strategy and enhance long-term profitability. The ultimate goal is not to eliminate costs, but to strategically manage them to achieve the optimal balance between risk mitigation and financial efficiency. Continued education and a proactive approach to risk management are essential for navigating the complexities of hedging and maximizing its potential benefits.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Hedging Costs . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.