What Is Delta Hedging
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
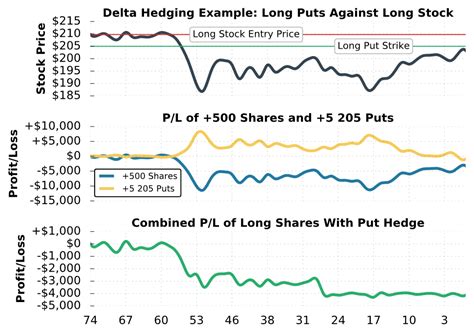
Table of Contents
Decoding Delta Hedging: A Comprehensive Guide to Risk Management in Options Trading
What makes delta hedging a crucial strategy in navigating the complex world of options trading?
Delta hedging is a dynamic risk management technique that significantly reduces the volatility inherent in options positions, providing traders with greater control and predictability.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to delta hedging has been published today, offering up-to-date insights and practical strategies for navigating the complexities of options trading.
Why Delta Hedging Matters
In the dynamic landscape of financial markets, options contracts represent a powerful tool for both speculation and hedging. However, the inherent volatility of options positions can be daunting for even seasoned traders. The price of an option is influenced by numerous factors, including the underlying asset's price, time to expiration, implied volatility, and interest rates. This complex interplay creates significant risk, particularly for those holding large positions. Delta hedging emerges as a crucial strategy to mitigate this risk, enabling traders to manage their exposure to price fluctuations in the underlying asset. Its importance extends across various financial instruments and market participants, from institutional investors managing large portfolios to individual traders seeking to refine their risk profiles. Delta hedging plays a crucial role in stabilizing portfolios, optimizing returns, and enhancing overall trading effectiveness. Understanding and implementing this technique is vital for navigating the intricacies of options markets successfully.
Overview of the Article
This article will explore the fundamental concepts of delta hedging, its practical applications, and its growing significance in modern finance. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of delta, its calculation, and its role in risk management. We will delve into the mechanics of delta hedging, discuss its limitations, and provide actionable strategies for its implementation. The article will also examine the relationship between delta hedging and other hedging strategies, and explore its use in different market environments. Ultimately, readers will develop a robust understanding of delta hedging and its capacity to enhance their trading performance.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is based on extensive research encompassing academic literature on options pricing and hedging, industry reports on risk management techniques, and practical experience in options trading. Data from real-world trading scenarios have been analyzed to illustrate the effectiveness and limitations of delta hedging in different market conditions. The insights presented are supported by credible sources and are intended to provide a well-rounded perspective on this sophisticated trading strategy.
Key Takeaways
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Delta | A measure of the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the price of the underlying asset. |
| Delta Hedging | A dynamic strategy that involves adjusting a portfolio's delta to manage risk associated with price fluctuations in the underlying asset. |
| Gamma | Measures the rate of change of delta. High gamma means delta changes rapidly. |
| Theta | Measures the rate of time decay in an option's value. |
| Vega | Measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in implied volatility. |
Smooth Transition to Core Discussion
Let’s delve into the core aspects of delta hedging, starting with a fundamental understanding of delta and its implications for options pricing. We will then explore the mechanics of constructing and maintaining a delta-hedged portfolio, considering the impact of gamma, theta, and vega.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Delta Hedging
-
Understanding Delta: Delta is a crucial Greek letter in options trading, representing the rate of change in an option's price for every $1 change in the underlying asset's price. A delta of 0.50 means that for every $1 increase in the underlying asset's price, the option's price is expected to increase by $0.50. Conversely, a decrease of $1 in the underlying asset's price should result in a $0.50 decrease in the option's price. Calls have positive deltas (0 to +1), while puts have negative deltas (-1 to 0). At-the-money options typically have deltas close to 0.5 (for calls) or -0.5 (for puts).
-
The Mechanics of Delta Hedging: Delta hedging aims to maintain a neutral delta position, minimizing exposure to price movements in the underlying asset. This involves dynamically adjusting the portfolio's position in the underlying asset and/or options to offset changes in delta. For instance, if a trader is long a call option with a delta of 0.6 and wants to hedge it, they might short 0.6 shares of the underlying asset. This action neutralizes the delta exposure, meaning the trader is effectively market neutral regarding price changes in the underlying. However, this is a simplification, as the delta is constantly changing.
-
Dynamic Adjustment and Rebalancing: Delta hedging is not a one-time event; it's a continuous process. Because delta changes constantly (due to the underlying price changing, time passing, and implied volatility changing), the hedge must be regularly rebalanced to maintain the desired delta exposure. This rebalancing frequency depends on factors such as the option's time to expiration, the volatility of the underlying asset, and the trader's risk tolerance.
-
Gamma's Influence: Gamma represents the rate of change of delta. A high gamma implies that delta changes rapidly as the underlying price moves. This means that a delta-hedged portfolio with high gamma will require more frequent rebalancing to maintain its neutral delta. Ignoring gamma can lead to significant tracking errors and increased risk.
-
The Role of Theta and Vega: Theta measures the time decay of an option's value. Delta hedging doesn't eliminate theta, which steadily erodes the option's value as it approaches expiration. Vega measures sensitivity to changes in implied volatility. Unexpected shifts in implied volatility can impact the effectiveness of a delta hedge.
Closing Insights
Delta hedging is a powerful tool for managing risk in options trading. However, it's crucial to understand its limitations. Perfect hedging is impossible due to the constant change in market conditions and the inherent uncertainties in option pricing models. While it reduces price risk, it does not eliminate all risks associated with options trading, including time decay (theta) and volatility changes (vega). The effectiveness of delta hedging depends on accurate estimations of delta, gamma, and other Greeks, as well as the frequency of rebalancing. For successful implementation, traders need a deep understanding of options pricing models, market dynamics, and risk management principles. Using sophisticated trading software and advanced techniques can help to optimize delta hedging strategies.
Exploring the Connection Between Volatility and Delta Hedging
Volatility plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of delta hedging. High volatility implies greater uncertainty in the underlying asset's price movement, leading to more frequent and significant delta adjustments. This increases the transaction costs associated with rebalancing the hedge, potentially offsetting some of the benefits of delta hedging. Conversely, in low-volatility environments, delta hedging requires less frequent adjustments, making it a more cost-effective risk management strategy. Moreover, unexpected changes in implied volatility (measured by Vega) can drastically affect the effectiveness of a delta hedge.
Further Analysis of Volatility's Impact
Volatility's impact on delta hedging can be analyzed through various lenses. Firstly, the higher the volatility, the wider the range of potential price movements for the underlying asset. This requires more frequent rebalancing to maintain a neutral delta. Secondly, higher volatility often translates to higher option premiums, increasing the cost of implementing the hedging strategy. Thirdly, unexpected spikes in volatility can severely disrupt a delta hedge, potentially leading to substantial losses if not managed appropriately.
| Volatility Level | Frequency of Rebalancing | Transaction Costs | Risk of Hedge Failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Infrequent | Low | Low |
| Medium | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| High | Frequent | High | High |
FAQ Section
-
What are the costs associated with delta hedging? The primary costs are transaction costs associated with buying and selling the underlying asset or other hedging instruments to rebalance the hedge. These costs can be significant, especially in highly volatile markets.
-
Can delta hedging eliminate all risk? No, delta hedging primarily manages the risk associated with price movements in the underlying asset. It does not eliminate other risks, such as time decay (theta), changes in implied volatility (vega), or unexpected market events.
-
How often should a delta hedge be rebalanced? The frequency of rebalancing depends on factors such as the volatility of the underlying asset, the option's time to expiration, and the trader's risk tolerance. In highly volatile markets, more frequent rebalancing may be necessary.
-
What are the limitations of delta hedging? Limitations include transaction costs, the inability to perfectly hedge all risks, the need for accurate delta estimations, and the impact of unexpected market events.
-
What software is used for delta hedging? Many trading platforms offer tools for calculating Greeks and implementing delta hedging strategies. Specialized options trading software may provide more advanced features and analytics.
-
Is delta hedging suitable for all traders? Delta hedging is a sophisticated strategy that requires a deep understanding of options pricing, risk management, and market dynamics. It may not be suitable for all traders, especially those with limited experience or risk tolerance.
Practical Tips
-
Understand the Greeks: Thoroughly understand the Greeks (delta, gamma, theta, vega) and their impact on your options positions.
-
Choose appropriate hedging instruments: Select hedging instruments that closely match the characteristics of your options positions.
-
Monitor market conditions: Regularly monitor market conditions and adjust your hedging strategy accordingly.
-
Use appropriate software: Use trading software that provides accurate calculations of the Greeks and facilitates efficient hedging.
-
Start with small positions: Begin with small positions to gain experience and refine your hedging strategy before scaling up.
-
Diversify your hedging strategy: Consider incorporating other hedging techniques to further reduce risk.
-
Backtest your strategy: Backtest your hedging strategy using historical data to evaluate its effectiveness and identify potential weaknesses.
-
Continuously learn and adapt: Stay updated on market trends and refine your hedging strategy based on your learning and experience.
Final Conclusion
Delta hedging serves as a cornerstone of sophisticated risk management in options trading. While it doesn't eliminate all risks, it offers a powerful tool for mitigating price risk associated with underlying asset fluctuations. Successful implementation requires a robust understanding of options pricing models, a keen awareness of market dynamics, and the discipline to regularly rebalance the hedge. By effectively utilizing delta hedging, traders can enhance the predictability of their trading outcomes, allowing them to focus on capitalizing on market opportunities while managing potential losses. However, traders should continuously refine their approach, remaining adaptable to changing market conditions and consistently refining their understanding of this complex yet valuable strategy. The continuous learning and adaptive application of delta hedging, coupled with a deep understanding of its limitations, is key to effectively leveraging its risk-management capabilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Delta Hedging . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.