Credit Enhancement Definition Benefits Techniques
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
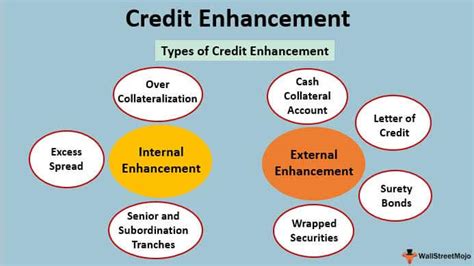
Table of Contents
Credit Enhancement: Unlocking Opportunities and Mitigating Risk
What makes credit enhancement a game-changer in today’s financial landscape?
Credit enhancement is reshaping the investment world by offering innovative solutions to bolster creditworthiness and unlock access to capital.
Editor’s Note: This article on credit enhancement was published today.
Why Credit Enhancement Matters
Credit enhancement is a critical element in today's complex financial markets. It plays a crucial role in reducing the risk associated with lending and investing, ultimately expanding access to capital for borrowers and providing investors with enhanced returns and security. In essence, it bridges the gap between creditworthy and less creditworthy borrowers, making otherwise unviable projects possible. The importance of credit enhancement is particularly evident in the municipal bond market, structured finance, and project finance where the inherent risk profile of the underlying asset often requires additional safeguards. Its application extends to various industries, fostering economic growth and development by enabling access to financing for infrastructure projects, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and other vital economic drivers.
Overview of the Article
This article explores the multifaceted nature of credit enhancement, encompassing its definition, benefits, and various techniques. We will delve into the mechanics of different enhancement methods, analyze their impact on credit risk, and examine real-world applications across various financial sectors. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how credit enhancement works, its advantages, and its limitations, ultimately enabling them to make more informed decisions regarding credit risk and investment opportunities.
Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The insights presented in this article are based on extensive research encompassing academic literature, industry reports, regulatory guidelines, and practical experience in the field of finance. We have analyzed numerous case studies, examined the performance of various credit enhancement techniques, and consulted expert opinions to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information provided. The analysis draws upon data from reputable sources, including rating agencies, financial institutions, and government publications.
Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Processes that improve the credit rating of an asset or obligation. |
| Benefits | Reduced borrowing costs, increased investor confidence, access to capital, enhanced project viability. |
| Techniques | Surety bonds, letters of credit, guarantees, collateralization, credit derivatives, insurance wraps. |
| Applications | Municipal bonds, structured finance, project finance, securitization, SME lending. |
| Risks & Considerations | Cost of enhancement, potential counterparty risk, complexity of structures, regulatory compliance issues. |
Let's dive deeper into the key aspects of credit enhancement, starting with its foundational principles and real-world applications.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Credit Enhancement
-
Defining Credit Enhancement: Credit enhancement refers to any mechanism used to improve the credit quality or rating of a debt obligation or asset. This is achieved by reducing the perceived risk associated with the underlying asset or liability. This improvement in creditworthiness typically translates to lower borrowing costs for the borrower and higher returns for investors.
-
Benefits of Credit Enhancement: The primary benefits of credit enhancement include:
- Reduced Borrowing Costs: By improving credit ratings, borrowers can secure loans at more favorable interest rates. This translates directly to cost savings.
- Increased Investor Confidence: Credit enhancement attracts a wider pool of investors by mitigating perceived risks and increasing the likelihood of repayment.
- Improved Access to Capital: Projects that might otherwise be considered too risky can become viable due to enhanced creditworthiness. This opens doors to financing for numerous ventures.
- Enhanced Project Viability: Credit enhancement can unlock funding for projects that contribute significantly to economic growth and development.
-
Techniques of Credit Enhancement: Several techniques are available for enhancing credit quality, each with its own characteristics and level of effectiveness:
- Surety Bonds: A third party (the surety) guarantees repayment of a debt obligation in the event of default by the borrower.
- Letters of Credit: Banks issue letters of credit, acting as a guarantee for the borrower's performance. If the borrower defaults, the bank covers the obligation.
- Guarantees: A third party (e.g., a parent company) promises to cover the borrower's debt in case of default.
- Collateralization: The borrower pledges assets (collateral) that can be liquidated to satisfy the debt in case of default.
- Credit Derivatives: These instruments transfer credit risk from the borrower to another party (e.g., through credit default swaps).
- Insurance Wraps: Insurance policies provide coverage for potential losses arising from default or other credit events.
-
Applications of Credit Enhancement: Credit enhancement is widely utilized in various sectors:
- Municipal Bonds: Credit enhancement is frequently employed to improve the creditworthiness of municipal bonds, making them more attractive to investors.
- Structured Finance: Credit enhancement plays a pivotal role in structured finance transactions, such as securitizations, by improving the credit rating of the resulting securities.
- Project Finance: Large-scale infrastructure projects often rely on credit enhancement to secure funding, given their inherent risks.
- Securitization: Pooling and repackaging of assets often requires credit enhancement to make the resulting securities more marketable.
- SME Lending: Credit enhancement can help small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) access financing by mitigating the higher risks associated with lending to these businesses.
-
Risks and Considerations: While credit enhancement offers substantial advantages, potential risks should be carefully considered:
- Cost of Enhancement: Implementing credit enhancement mechanisms involves fees and costs that can impact overall profitability.
- Counterparty Risk: The effectiveness of credit enhancement depends on the creditworthiness of the guarantor or insurer. If the guarantor defaults, the enhancement is ineffective.
- Complexity of Structures: Some credit enhancement mechanisms can be complex and challenging to understand, leading to potential misunderstandings and misinterpretations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Implementing credit enhancement mechanisms must adhere to regulatory requirements, which can vary across jurisdictions.
Closing Insights
Credit enhancement is a vital tool in mitigating credit risk and fostering access to capital. Its application across various financial sectors has significantly impacted the efficiency and stability of markets. By understanding the various techniques, benefits, and potential risks associated with credit enhancement, investors and borrowers can make better-informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the financial landscape. The ongoing evolution of credit enhancement mechanisms reflects the dynamic nature of financial markets and the continuous search for innovative solutions to manage and reduce risk.
Exploring the Connection Between Credit Ratings and Credit Enhancement
Credit ratings play a central role in determining the efficacy of credit enhancement. A higher credit rating generally translates to lower borrowing costs and increased investor confidence. Credit enhancement directly influences credit ratings by reducing the perceived risk associated with the underlying asset or obligation. For example, a highly-rated surety bond can significantly improve the credit rating of a municipal bond, even if the issuer itself has a lower rating. The connection between credit ratings and credit enhancement is symbiotic: credit enhancement seeks to improve ratings, which in turn attracts investors and lowers borrowing costs.
Further Analysis of Credit Ratings
Credit ratings are assessments of the creditworthiness of borrowers or issuers of debt. They are typically assigned by credit rating agencies (CRAs) based on an analysis of various factors, including the borrower's financial strength, the nature of the debt, and the prevailing economic conditions. Credit ratings range from the highest investment-grade ratings (AAA, AA, A) down to speculative-grade ratings (BB, B, CCC, etc.), with each rating reflecting a different level of risk. The ratings directly affect the interest rates charged to borrowers and the returns demanded by investors. A higher rating translates to lower interest rates and higher investor confidence. A lower rating leads to higher interest rates and potentially limited access to capital.
| Credit Rating Category | Description | Interest Rate | Investor Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Investment Grade | Low risk of default | Lower | High |
| Speculative Grade | Higher risk of default | Higher | Lower |
FAQ Section
-
What is the difference between a guarantee and a surety bond? While both involve a third party guaranteeing repayment, a surety bond is typically issued by a licensed surety company, while a guarantee can be provided by a variety of entities, including parent companies or other financially strong organizations.
-
How does collateralization enhance credit? Collateral provides a tangible asset that can be liquidated in case of default, reducing the lender’s risk and thereby enhancing the credit quality of the loan.
-
What are credit default swaps (CDS)? CDSs are credit derivatives that transfer the credit risk associated with a debt instrument from one party to another. The buyer of a CDS pays a premium in exchange for protection against default.
-
Is credit enhancement always necessary? No. Credit enhancement is only needed when the underlying asset or obligation has a credit rating that is not sufficient to attract the desired level of investment or to secure financing at acceptable rates.
-
What are the potential downsides of credit enhancement? The primary downsides are the costs associated with implementing the enhancement and the risk that the guarantor or insurer may themselves default.
-
How are credit enhancement structures regulated? The regulation of credit enhancement structures varies depending on the specific type of enhancement and the jurisdiction involved. However, most jurisdictions have regulations aimed at ensuring transparency, protecting investors, and preventing market abuse.
Practical Tips
-
Assess your creditworthiness: Before seeking credit enhancement, thoroughly assess your credit profile to understand the areas that need improvement.
-
Explore different enhancement options: Compare the costs and benefits of different credit enhancement techniques to determine the most appropriate option for your specific needs.
-
Select a reputable guarantor or insurer: If using a surety bond, guarantee, or insurance wrap, choose a provider with a strong credit rating and proven track record.
-
Understand the terms and conditions: Carefully review all the terms and conditions associated with any credit enhancement agreement before signing.
-
Comply with regulatory requirements: Ensure your credit enhancement structure complies with all applicable regulations.
-
Monitor performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your credit enhancement mechanism to ensure it continues to meet your needs.
-
Seek professional advice: Consult with experienced financial professionals to guide you through the complex process of selecting and implementing a credit enhancement strategy.
-
Transparency and disclosure: Maintain transparency regarding the credit enhancement mechanism used, including its costs and limitations.
Final Conclusion
Credit enhancement is a powerful tool for mitigating risk and improving access to capital. Its various techniques, carefully chosen and implemented, can transform potentially risky ventures into viable investment opportunities. By understanding its principles, benefits, and limitations, borrowers and investors can make informed decisions, enhancing their financial strategies and contributing to a more stable and resilient financial system. The ongoing innovation in this field will continue to shape the future of finance, providing increasingly sophisticated solutions to manage credit risk in a constantly evolving global economy.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Credit Enhancement Definition Benefits Techniques . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.